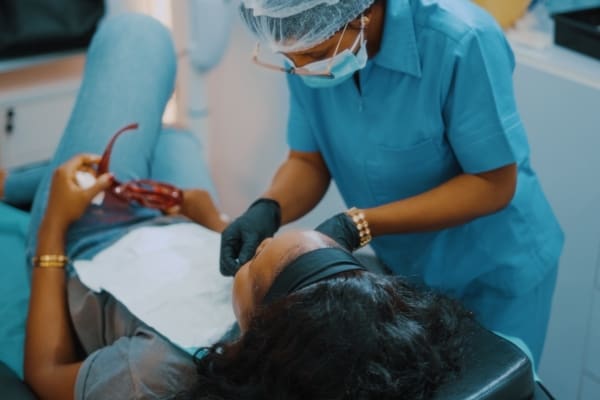
Oral cancer is a serious disease that affects thousands of people each year. It’s a type of cancer that can develop in any part of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, gums, and throat. Unfortunately, oral cancer is often not diagnosed until it has progressed to a more advanced stage, which can make it more difficult to treat.
That’s why oral cancer screenings are so important. These screenings are a simple and painless way for dentists and doctors to check for signs of oral cancer in their patients. During a screening, the healthcare provider will examine your mouth and throat for any abnormalities or unusual growths. If they find anything suspicious, they may recommend further testing or a biopsy to determine if it’s cancerous.
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a type of cancer that can develop in any part of the mouth, including the tongue, lips, gums, cheeks, and roof and floor of the mouth. It usually begins as a small, painless lesion or abnormality and can progress into a tumor.
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
The symptoms of oral cancer can be difficult to detect in the early stages, which is why regular oral cancer screenings are so important. Some of the most common symptoms of oral cancer include:
- Sores or ulcers in the mouth that do not heal within two weeks
- Red or white patches on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth
- Swelling or lumps in the mouth, neck, or throat
- Difficulty speaking, chewing, or swallowing
- Persistent earaches or headaches
- Numbness or loss of feeling in the face or mouth
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Several factors can increase the risk of developing oral cancer, including:
- Tobacco use, including smoking and chewing tobacco
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Exposure to human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Prolonged sun exposure to the lips
- Poor oral hygiene
- A weakened immune system
- Family history of cancer
It is important to note that not all cases of oral cancer are linked to these risk factors, and some people with no known risk factors can still develop oral cancer. Regular oral cancer screenings can help detect any abnormalities or precancerous lesions early, which can improve the chances of successful treatment.
The Importance of Oral Cancer Screenings
Regular oral cancer screenings are an essential part of maintaining good oral health. Early detection of oral cancer can increase the chances of successful treatment and improve the patient’s survival rate.
What are Oral Cancer Screenings?
Oral cancer screenings are examinations performed by dental professionals to look for signs of cancer or precancerous conditions in the oral cavity. These screenings are typically painless and non-invasive.
Who Should Get Oral Cancer Screenings?
Everyone should get oral cancer screenings, regardless of age or risk factors. However, individuals who use tobacco products, consume alcohol heavily, have a family history of oral cancer, or have previously had oral cancer are at a higher risk and should be screened more frequently.
How Often Should You Get Oral Cancer Screenings?
The frequency of oral cancer screenings depends on the patient’s risk factors. For individuals with a low risk of oral cancer, screenings should be performed at least once a year. Patients with a higher risk of oral cancer should be screened more frequently, as recommended by their dentist or doctor.
What Happens During an Oral Cancer Screening?
During an oral cancer screening, a dental professional will examine the oral cavity for any abnormalities, such as lesions, lumps, or discolorations. The screening may also include a physical exam of the neck and lymph nodes. If an abnormality is found, the dental professional may recommend a biopsy to determine if it is cancerous.
What Happens if an Abnormality is Found During an Oral Cancer Screening?
If an abnormality is found during an oral cancer screening, the patient may be referred to a specialist for further evaluation and treatment. Early detection of oral cancer is crucial, as it can significantly improve the patient’s chances of successful treatment and survival.
Additional Tests
In addition to oral cancer screenings, dental professionals may also recommend other tests, such as a salivary gland biopsy or imaging tests, to further evaluate any abnormalities found during the screening.
In conclusion, oral cancer screenings are an essential part of maintaining good oral health and should be performed regularly, as recommended by dental professionals. Early detection of oral cancer can significantly improve the patient’s chances of successful treatment and survival. If you have any concerns about oral cancer, make an appointment with your doctor or dental hygienist today.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Prevention is key when it comes to oral cancer. While there’s no surefire way to prevent oral cancer, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. In this section, we’ll discuss some prevention tips, lifestyle changes, and education and awareness to help you stay healthy.
Prevention Tips
The American Cancer Society recommends a few tips to help prevent oral cancer:
- Avoid tobacco use: Cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and chewing tobacco all increase your risk of oral cancer. If you use tobacco, quitting is the best thing you can do for your health.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol use is another risk factor for oral cancer. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Protect yourself from HPV: HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause oral cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about the HPV vaccine, which can help protect against certain strains of the virus.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brush and floss your teeth regularly, and visit your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to the prevention tips above, making some lifestyle changes can also help reduce your risk of oral cancer:
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce your risk of cancer.
- Protect yourself from sun exposure: Lips are particularly vulnerable to sun damage, which can increase your risk of oral cancer. Wear a lip balm with SPF and a hat when you’re outside.
- Quit smoking: If you smoke, quitting is the best thing you can do for your health. Talk to your healthcare provider about resources to help you quit.
Education and Awareness
Education and awareness are also important when it comes to oral cancer prevention. Some things to keep in mind:
- Know your risk factors: Talk to your healthcare provider about your risk factors for oral cancer, and get screened regularly if you’re at higher risk.
- Know the signs and symptoms: Oral cancer can often be detected early if you know what to look for. Some signs and symptoms to watch for include sores that don’t heal, lumps or bumps in your mouth, and difficulty swallowing.
- Spread the word: Help raise awareness about oral cancer by sharing information with your friends and family.
Treatment and Cure
Treatment Options
The treatment for oral cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of cancer, location, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. The most common treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Surgery is often the first-line treatment for oral cancer. The goal of surgery is to remove the cancerous mass and any nearby lymph nodes that may be affected. Depending on the location and stage of the cancer, the surgery may involve removing part of the tongue, jawbone, or other structures in the mouth and throat.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy. Radiation therapy is often used to treat cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes in the neck.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with surgery or radiation therapy. Chemotherapy is often used to treat advanced-stage oral cancer.
Targeted therapy is a newer type of cancer treatment that targets specific molecules that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
Cure Rates
The cure rate for oral cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of cancer, location, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. According to the American Cancer Society, the overall five-year survival rate for oral cancer is about 65%. However, the survival rate varies widely depending on the stage of cancer at diagnosis. For example, the five-year survival rate for localized oral cancer is about 84%, while the five-year survival rate for oral cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body is only about 39%.
Benefits of Early Detection
Early detection is crucial for the successful treatment of oral cancer. When oral cancer is detected early, it is more likely to be treatable and may even be curable. Regular oral cancer screenings can help detect early signs of cancer, such as numbness, irritation, or hoarseness. People who are at an increased risk of oral cancer, such as those who use tobacco or alcohol, should have regular oral cancer screenings.
In addition to regular screenings, people can also reduce their risk of developing oral cancer by avoiding tobacco and alcohol use, maintaining good oral hygiene, and eating a healthy diet. If oral cancer is detected, a prompt analysis and laboratory testing can help determine the best course of treatment.



